Latest posts
Magazine
Multiple sclerosis: These micronutrients can support treatment
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease. Immune cells attack the nerve fibers and destroy the myelin sheath. This is an insulating protective layer that ensures rapid signal transmission. Nerve cells in the spinal cord and brain are damaged by chronic inflammation.
Typical symptoms of multiple sclerosis are:
Concentration and memory disorders
Tingling and numbness
Coordination disorders and unsteady gait
Chronic fatigue
Muscle cramps
The causes of multiple sclerosis are not well understood. Certain viral infections, vitamin D deficiency, smoking, obesity and a disturbed intestinal flora seem to promote multiple sclerosis
Treatment primarily involves anti-inflammatory drugs to control the inflammatory reactions.
Micronutrients can support the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D regulates the immune system and can thus counteract inflammation. Vitamin D deficiency is linked to the progression of MS: the poorer the vitamin D supply, the faster the disease progresses. [1]
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are useful for multiple sclerosis for several reasons. Firstly, they have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. They are also part of the myelin sheath and have a nerve-protecting effect. [2]
Antioxidants: Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Zinc, Selenium
People with multiple sclerosis often have elevated markers for oxidative stress. At the same time, they are often not supplied with enough antioxidants. In particular, fat-soluble vitamins with antioxidant effects such as vitamin A and vitamin E are easily lacking.
Vitamin C , vitamin E, zinc and selenium are important antioxidants in the body. Zinc also has important functions in the nervous system. For example, it is needed to maintain the myelin sheath. [3]
Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 has important functions in energy metabolism. It is needed for energy production in the mitochondria – the power plants of our cells. [4]
Coenzyme Q10 is also an antioxidant, which can counteract oxidative stress.
Mitochondria appear to play an important role in multiple sclerosis: they are often faulty and do not function optimally. This contributes to exhaustion. Coenzyme Q10 levels are often too low in multiple sclerosis. Conversely, studies suggest that taking coenzyme Q10 could actually alleviate symptoms.
L-carnitine is also essential for mitochondrial function. Patients with multiple sclerosis often have low L-carnitine levels. However, the data available here is not as good as for coenzyme Q10.
B vitamins
B vitamins are also known as nerve vitamins because they perform many important functions in the nervous system. Vitamin B12, for example, is essential for maintaining myelin.
In addition, B vitamins are needed to break down homocysteine . Homocysteine is a toxic metabolic product. If there is a lack of B vitamins, the homocysteine level rises. Vitamin B6, folic acid (vitamin B9) and vitamin B12 are particularly important here. Homocysteine promotes inflammation and can damage the nervous system.
In patients with multiple sclerosis, homocysteine levels are often elevated and folic acid and vitamin B12 are often deficient. [5]
magnesium
Magnesium is important for the muscles and promotes their relaxation. Magnesium also has important functions in energy metabolism. Studies suggest that magnesium in combination with vitamin D and calcium could counteract the progression of multiple sclerosis. [6]
Alpha-lipoic acid
Alpha-lipoic acid is an effective antioxidant and also has anti-inflammatory effects. In addition, alpha-lipoic acid has a nerve-protective effect and can promote nerve regeneration. [7]
In multiple sclerosis, alpha-lipoic acid can lower inflammatory markers.
Probiotics
A healthy intestinal flora is very important for the intestines. A good ratio between "good" and harmful bacteria also helps to counteract inflammation. In a small study, taking probiotics in multiple sclerosis was able to reduce inflammation levels. [8] However, more research is needed here.
Conclusion: Antioxidants are promising in multiple sclerosis
Oxidative stress and inflammation contribute to the development and progression of multiple sclerosis. A good supply of anti-inflammatory nutrients and antioxidants is likely to be helpful in multiple sclerosis. Sufferers should also ensure they have an adequate supply of nutrients that are important for nerve function.
WE HAVE GONE YOU A 10% VOUCHER FOR OUR
OMEGA-3 , VITAMIN B , COENZYME Q10 ,MAGNESIUM , VITAMIN D , VITAMIN C , ZINC AND SELENIUM
PROVIDED AND HOPE TO BRING YOU JOY WITH IT.
SIMPLY COPY THE FOLLOWING COUPON CODE
AND ENTER IT AT CHECKOUT:
MS+V10
TO THE PRODUCTS
[1] https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD008422.pub3/full
[2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7860710
[3] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4904428/
[4] https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Coenzyme-Q10-in-the-Treatment-of-Mitochondrial-Neergheen-Chalasani/fe646f7790e1beb346019a9219c3a5ffd99d1047?p2df
[5] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4904428/
[6] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3537648/
[7] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5840773/
[8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6213508/
What effect can micronutrients have on arteriosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis (also called atherosclerosis) causes hardening and thickening of blood vessels. Colloquially, this is also referred to as hardening of the arteries.
Deposits narrow the vessels that supply the organs with oxygen-rich blood. This causes the blood vessels to narrow and a blood clot can impede or even completely stop the blood flow. This means that vital organs are no longer supplied with oxygen, which can cause a heart attack or stroke. In the worst case, this can have fatal consequences.
Anticoagulants are often used to treat arteriosclerosis. These reduce the risk of blood clots. Cholesterol-lowering drugs are also often prescribed, as high cholesterol levels are considered a risk factor for arteriosclerosis.
Diet also plays an important role in arteriosclerosis. Diet-related problems such as obesity, high blood pressure and diabetes are the greatest risk factors for arteriosclerosis. Treating these can counteract the progression of arteriosclerosis.
The diet also provides many important nutrients that play a role in arteriosclerosis.
Micronutrients can also support the treatment of arteriosclerosis.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have an anti-inflammatory effect. Since inflammation can promote arteriosclerosis, it makes sense to keep inflammation in check.
Studies suggest that a good supply of omega-3 fatty acids can actually reduce the risk of heart attack. [1]
magnesium
Magnesium is very important for nerve and muscle function. In addition, a good supply of magnesium can help regulate blood pressure. [2] High blood pressure damages the blood vessels and can promote arteriosclerosis.
Vitamin K2
A good supply of vitamin K2 is very important for vascular health. It also ensures that calcium is absorbed from the blood into the bones. [3] Too high a calcium level can further damage the vessels.
OPC
High LDL cholesterol is particularly problematic when it oxidizes. Then it promotes the formation of plaques. Oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPC) are extracted from grape seeds and are very effective antioxidants. Studies indicate that taking OPC could reduce the oxidation of LDL. [4]
Zinc, selenium, vitamin C and vitamin E
In addition to OPC, there are other important antioxidants that are even essential nutrients, which means that we have to consume them through food.
These primarily include zinc , selenium , vitamin C and vitamin E.
B vitamins
B vitamins are needed to break down the metabolic product homocysteine. Vitamin B6, folic acid (vitamin B9) and vitamin B12 are particularly important here. If one or more of these vitamins are lacking, the homocysteine level rises. A high homocysteine level damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of arteriosclerosis.
In the case of arteriosclerosis, it is therefore important to ensure a good supply of B vitamins.
Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 plays a central role in energy production. Coenzyme Q10 is also an important antioxidant. Coenzyme Q10 is also important for heart health and can improve the heart's ability to contract. [5]
Coenzyme Q10 is also useful when taking statins (so-called cholesterol-lowering drugs) because coenzyme Q10 can reduce the side effects.
Conclusion: Deficiencies promote arteriosclerosis
Deficiencies in certain nutrients can promote arteriosclerosis. People with arteriosclerosis or at increased risk should ensure they have a good supply of these nutrients.
WE HAVE GONE YOU A 10% VOUCHER FOR OUR
OMEGA-3 , VITAMIN B , COENZYME Q10 ,MAGNESIUM , OPC , VITAMIN K , VITAMIN C , ZINC AND SELENIUM
PROVIDED AND HOPE TO BRING YOU JOY WITH IT.
SIMPLY COPY THE FOLLOWING COUPON CODE
AND ENTER IT AT CHECKOUT:
ARTERIO+V10
TO THE PRODUCTS
[1] https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2530286
[2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3683817/
[3] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18722618/
[4] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17616006/
[5] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27333901/

Alzheimer's: This is the role nutrients play in treatment
Alzheimer's is the most common form of dementia. Nerve cells die and the brain shrinks. This leads to forgetfulness, memory problems and disorientation. The disease usually begins after the age of 65.
The cause of Alzheimer's is not clearly understood. Oxidative stress, high levels of heavy metals and high homocysteine levels appear to promote the disease. Lifestyle also plays a role in the development of Alzheimer's. People who eat an unhealthy diet and do not exercise enough have an increased risk of Alzheimer's.
Alzheimer's disease causes protein deposits in the brain, known as beta-amyloid plaques. These were long considered to be the cause of Alzheimer's disease and many treatment approaches aim to reduce these plaques in the brain. However, recent data cast doubt on this theory. [1]
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are often used to treat Alzheimer's. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter in the brain that is important for memory formation. The esterase enzyme breaks down acetylcholine. If this enzyme is inhibited, the acetylcholine concentration in the brain increases, which can improve memory performance.
Behavioral therapy and nutrition also play a role in Alzheimer's treatment.
Micronutrients can also support the treatment of Alzheimer's.
B vitamins
B vitamins are very important for the functioning of nerve cells. They are also needed to break down the toxic metabolic product homocysteine . Vitamin B6, folic acid (vitamin B9) and vitamin B12 are particularly important here. If you are not getting enough of these B vitamins, your homocysteine level will rise.
High homocysteine levels cause inflammation and oxidative stress and promote atherosclerosis. It also increases the risk of Alzheimer's disease. [2]
A dietary supplement with B vitamins is particularly promising in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease, especially when there is a poor supply of B vitamins.
Curcumin
Curcumin is known for its antioxidant effect. Studies have shown that curcumin can improve memory and attention in healthy people. [3] However, its effectiveness in Alzheimer's disease has not yet been clearly proven.
Vitamin C and Vitamin E
The brains of Alzheimer's patients usually show major oxidative damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants scavenge free radicals and protect against oxidative stress. Vitamin C and vitamin E are two important antioxidants in the body. [4] There is evidence that a diet rich in antioxidants could protect against Alzheimer's.
selenium
Selenium is a component of antioxidant enzymes. Low selenium levels are suspected of promoting Alzheimer's. However, it has not yet been clearly shown that Alzheimer's patients benefit from taking selenium. [5]
Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 is also an important antioxidant. It also has important functions in energy metabolism and is needed to generate energy in the mitochondria (the power plants of the cell). Alzheimer's patients often have too low a coenzyme Q10 level. [6]
Vitamin D
Vitamin D performs many important functions in the body that are relevant to Alzheimer's. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, is important for vascular health and protects nerve cells. A vitamin D deficiency is associated with a decline in mental abilities. In Alzheimer's, patients with low vitamin D levels have greater memory problems than patients with good vitamin D levels. [7]
Vitamin D deficiency is widespread in Germany and older people are even more affected than younger people.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have an anti-inflammatory effect and are very important for the function of nerve cells. A poor supply of the omega-3 fatty acid DHA is associated with a decline in mental abilities. People who regularly eat fish and are well supplied with omega-3 fatty acids are less likely to suffer from Alzheimer's than people who are deficient in omega-3 fatty acids. [8]
Conclusion: Nutrients can protect nerve cells
Nerve cells require many nutrients to function optimally. A lack of certain nutrients appears to increase susceptibility to Alzheimer's. A good supply of essential, critical nutrients may help prevent Alzheimer's. In any case, it makes sense to avoid a deficiency in essential nutrients.
WE HAVE GONE YOU A 10% VOUCHER FOR OUR
VITAMIN D , TURMERIC EXTRACT , OMEGA-3 , VITAMIN B , COENZYME Q10 , VITAMIN C AND SELENIUM
PROVIDED AND HOPE TO BRING YOU JOY WITH IT.
SIMPLY COPY THE FOLLOWING COUPON CODE
AND ENTER IT AT CHECKOUT:
ALZHEIMER+V10
TO THE PRODUCTS
.
[1] https://www.alzheimer-forschung.de/aktuelles/melde/aufregung-in-der-alzheimer-forschung-was-ist-dran-an-den-beta-amyloid-faelschungen/
[2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5836397/
[3] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30084334/
[4] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11461772/
[5] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5506489/
[6] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19907182/
[7] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29998819/
[8] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30084334/
What effect can micronutrients have on chronic inflammatory bowel disease?
Chronic inflammatory bowel disease is characterized by recurring inflammation in the intestine. Typical symptoms are abdominal pain, flatulence and diarrhea. Constipation and bloody stools are also common.
This results in digestive disorders and often nutrient deficiencies. People with chronic inflammatory bowel disease also have an increased risk of colon cancer.
The causes of chronic inflammatory bowel disease are not well understood. The intestinal barrier is disrupted, allowing bacteria from the intestine to penetrate through the intestinal mucosa. This leads to inflammatory reactions.
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are among the most common chronic inflammatory bowel diseases.
In ulcerative colitis, the inflammation affects the rectum. In Crohn's disease, the part between the small intestine and the large intestine is usually affected. Sometimes the rest of the gastrointestinal tract is also inflamed.
In chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, anti-inflammatory drugs are used to reduce inflammation.
In the acute phases, which are called attacks, cortisone is used to suppress the immune system.
Micronutrients can support treatment and help keep inflammation under control. In addition, people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease have an increased need for nutrients. This is because the inflammation means that nutrients are not absorbed as well in the intestine, which can easily lead to deficiencies. Those affected should therefore ensure that they have an adequate supply of essential nutrients.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D inhibits inflammatory messengers and thus counteracts inflammation.
Unfortunately, vitamin D deficiency is very common and people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease are particularly affected. [1] You should therefore pay particular attention to ensuring you have a good vitamin D supply.
Probiotics
In chronic inflammatory bowel disease, the intestinal flora is often disturbed. Researchers suspect that dysbiosis in the intestine can cause or at least promote inflammatory bowel disease.
Beneficial bacteria can displace pathogenic, inflammatory bacteria. They can also strengthen the intestinal barrier and regulate the immune system.
Taking probiotics can therefore support the treatment of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. [2]
Curcumin
Curcumin is extracted from turmeric and is known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Initial studies suggest that curcumin could also reduce inflammation in Crohn’s disease. [3]
B vitamins
B vitamins have important functions in energy metabolism and are needed for cell division. They can therefore support repair processes in the intestine.
In addition, B vitamins are needed to break down the metabolic product homocysteine. People with Crohn's disease often have elevated homocysteine levels . [4]
Antioxidants
The body has many defense mechanisms against inflammation and oxidative stress. However, it needs antioxidant nutrients to do this. These primarily include vitamin A, vitamin C , vitamin E, zinc and selenium . People with chronic inflammatory bowel disease are often not well supplied with these nutrients. [5] [6]
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have an anti-inflammatory effect. A good supply of omega-3 fatty acids is therefore particularly important for inflammatory diseases. Studies indicate that omega-3 fatty acids can also be helpful in inflammatory bowel diseases. [7]
Glutamine
The cells of the small intestinal mucosa require a lot of glutamine. A lack of glutamine makes the intestinal mucosa permeable to pathogens, which can increase inflammation.
Taking glutamine can therefore strengthen the intestinal barrier. In a study with Crohn's disease patients, glutamine was able to reduce intestinal permeability. [8] Collagen is a good source of glutamine.
Conclusion: Nutrients can counteract inflammation in the intestine
There are many nutrients that have an anti-inflammatory effect. People with chronic inflammatory bowel disease should pay particular attention to ensuring they have a good supply of these nutrients.
WE HAVE GONE YOU A 10% VOUCHER FOR OUR
VITAMIN D , CURCUMA EXTRACT , OMEGA-3 , VITAMIN B , VITAMIN C , ZINC AND SELENIUM
PROVIDED AND HOPE TO BRING YOU JOY WITH IT.
SIMPLY COPY THE FOLLOWING COUPON CODE
AND ENTER IT AT CHECKOUT:
CROHN+V10
TO THE PRODUCTS
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4427008/
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28294322/
[3] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23076948/
[4] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23591663/
[5] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12591053/
[6] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27916926/
[7] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26752948/
[8] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22038507/

Prevent cystitis with home remedies and nutrients
A bladder infection is caused by bacteria in the bladder. This leads to inflammation in the urethra and bladder. Bladder infections are extremely unpleasant: urination is painful and there are problems with urination.
Stress and cold can promote bladder infections. People with diabetes have a higher risk of urinary tract infections. Sometimes bacteria can enter the bladder during medical procedures, which can lead to infections. This risk exists during cystoscopies, bladder irrigation and bladder catheters.
Women are significantly more likely to suffer from bladder infections than men. The risk is particularly high during menopause and pregnancy.
Acute cystitis often needs to be treated with antibiotics. However, frequent use of antibiotics is problematic because it negatively affects the intestinal and vaginal flora and promotes antibiotic resistance.
There are some micronutrients and home remedies that can help prevent bladder infections.
Cranberry extract
Cranberries contain certain secondary plant substances called proanthocyanidins. These prevent bacteria from settling in the mucous membrane of the urinary tract.
The effectiveness of cranberry extract in acute cystitis is not clearly proven. However, there is good evidence that cranberry extract can help prevent cystitis. [1] People with frequently recurring urinary tract infections can therefore benefit from cranberry extract.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is essential for the immune system. Therefore, it can also support the immune system in the fight against bacteria that cause cystitis.
In addition, vitamin C is acidic and can therefore acidify the urine. Bacteria cannot multiply as well in an acidic environment. [2]
Vitamin D
Vitamin D has important functions in the immune system. Vitamin D also stimulates the production of defense molecules in the urine, which ensure that bacteria cannot attach themselves so easily to the bladder wall.
Studies have shown that people with vitamin D deficiency are more susceptible to bladder infections. [3] In a study with diabetes patients, taking 20,000 IU weekly was able to reduce the frequency of bladder infections. [4]
zinc
Zinc is also essential for the immune system. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, promotes the production of antibodies and can increase the activity of certain immune cells.
People with low zinc levels have an increased risk of bladder infections. [5] However, there are few studies on taking zinc for urinary tract infections. In one study, children who took zinc recovered more quickly from a bladder infection than the control group that did not receive zinc.
selenium
A well-functioning immune system needs sufficient selenium . Selenium has an anti-inflammatory effect and captures free radicals.
Unfortunately, there are no studies on selenium for cystitis, but there is evidence that selenium may be helpful for bacterial infections. [6]
Amino acid methionine
Methionine is one of the essential amino acids that we must consume through our diet. In the case of bladder infections, it has the useful property of acidifying the urine. This means that bacteria cannot multiply as easily.
In one study, taking methionine reduced the recurrence rate of cystitis. [7]
Conclusion: A healthy immune system can prevent bladder infections
Cystitis is caused by bacteria. A healthy immune system is essential in the fight against bacterial infections. The immune system needs many nutrients. If these are missing, we become more susceptible to infections. Anyone who is susceptible to cystitis should therefore ensure that they have a good supply of these nutrients.
WE HAVE GONE YOU A 10% VOUCHER FOR OUR
VITAMIN C , VITAMIN D , ZINC AND SELENIUM
PROVIDED AND HOPE TO BRING YOU JOY WITH IT.
SIMPLY COPY THE FOLLOWING COUPON CODE
AND ENTER IT AT CHECKOUT:
BLASE+V10
TO THE PRODUCTS
[1] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32752183/
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17611821/
[3] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30814089/
[4] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27357103/
[5] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31456957/
[6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4288282/
[7] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9446004/
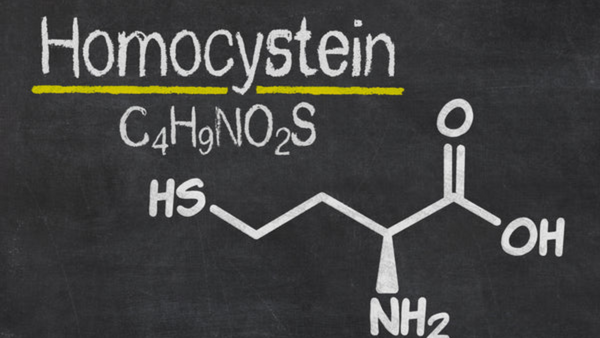
Elevated homocysteine: Lower homocysteine with nutrients
A high homocysteine level increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, arteriosclerosis and thrombosis. Homocysteine is also suspected of being involved in the development of dementias such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
Homocysteine is a toxic metabolic product that the body must break down to render it harmless.
An increased homocysteine level is often due to a poor supply of B vitamins, which are needed to break down homocysteine.
Kidney problems can also lead to high homocysteine levels, as homocysteine cannot be excreted well via the kidneys when kidney function is impaired.
Certain medications, such as the Parkinson's drug L-Dopa, antiepileptics and cholesterol-lowering drugs can also increase homocysteine levels.
The following nutrients can help lower homocysteine levels:
B vitamins
The body needs some B vitamins to detoxify homocysteine. If there is a deficiency of these B vitamins, homocysteine levels increase. The most important ones here are vitamin B6, folic acid (vitamin B9) and vitamin B12 .
Vitamin B6 is needed for the conversion of homocysteine to cysteine.
Folic acid promotes the regeneration of the enzyme responsible for the breakdown of homocysteine.
With the help of vitamin B12, homocysteine is converted into the amino acid methionine.
It is well documented that B vitamins can lower homocysteine levels. However, the health benefits are not quite as well documented.
However, initial studies show that taking folic acid and vitamin B6 can reduce the risk of stroke. 1
In some studies, B vitamins have been shown to reduce the risk of nerve damage in diabetes. 2
Choline and betaine
Choline and betaine support the function of B vitamins. They provide methyl groups that are needed for the conversion of homocysteine into methionine. A good supply of choline and betaine is associated with low homocysteine levels.
In one study, choline in the form of phosphatidylcholine was able to lower homocysteine levels. 3
Something similar could be shown for betaine. 4
Because choline and betaine work so closely with B vitamins, many vitamin B complexes contain choline and betaine in addition to B vitamins.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory and vascular protective effects. But that's not all. They can also lower homocysteine levels. 5 The mechanism is not fully understood, but scientists suspect that omega-3 fatty acids have a positive effect on methionine metabolism.
Conclusion: Too much homocysteine is dangerous
Homocysteine is a metabolic product that is not problematic in normal amounts. However, elevated homocysteine levels are dangerous and increase the risk of many diseases. B vitamins and other nutrients have critical functions in homocysteine metabolism.
WE HAVE GONE YOU A 10% VOUCHER FOR OUR
VITAMIN B COMPLEX , VITAMIN B12 AND OMEGA-3
PROVIDED AND HOPE TO BRING YOU JOY WITH IT.
SIMPLY COPY THE FOLLOWING COUPON CODE
AND ENTER IT AT CHECKOUT:
STOFFWECHSEL+V10
TO THE PRODUCTS
1 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32503038/
2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20937919/
3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16002808/
4 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33764214/
5 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26420180/

Neurodermatitis: What can micronutrients do?
Neurodermatitis is characterized by eczema: the skin is inflamed and rashes occur.
External and internal factors appear to play a role in the development of neurodermatitis. Pollutants, allergies, stress and an unhealthy diet can cause the immune system to overreact, resulting in inflammatory skin reactions.
Hormonal changes, stress, the climate, allergens, infections and a sick intestine are factors that can promote neurodermatitis.
Anti-inflammatory drugs such as cortisone preparations, ciclosporin and calcineurin inhibitors are used to treat neurodermatitis.
Micronutrients can support the treatment of neurodermatitis.
zinc
Zinc is extremely important for healthy skin. It promotes wound healing and skin renewal. It also has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties and thus promotes the body's defense against pathogens.
It is therefore not surprising that zinc deficiency can promote skin diseases. A poor supply of zinc is also associated with the development of neurodermatitis.
In one study, taking zinc significantly improved the skin condition of neurodermatitis patients. 1
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have an anti-inflammatory effect. Most people do not get enough of omega-3 fatty acids in their diet.
Unfortunately, there is not much research on omega-3 fatty acids for atopic dermatitis. However, in a small study, taking omega-3 fatty acids was able to alleviate the symptoms of eczema. 2
Vitamin D
People with vitamin D deficiency have an increased risk of neurodermatitis. In countries with lots of sun, neurodermatitis is also less common. Vitamin D deficiency is very common in Germany. According to a study by the Robert Koch Institute, over half of Germans do not have an adequate supply of vitamin D.
Vitamin D has an immune-regulating effect and can therefore counteract inflammation. For many neurodermatitis patients, the symptoms are more pronounced in winter than in summer. This is another indication that vitamin D supply could play a role in neurodermatitis.
In a study of children with atopic dermatitis, symptoms decreased significantly after one month of vitamin D intake. 3 4
Antioxidants
The inflammation in neurodermatitis promotes the formation of free radicals, which cause oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can in turn increase inflammation.
Neurodermatitis patients are often not well supplied with antioxidant nutrients. In addition, markers for oxidative stress are often elevated.
Vitamin E helps to reduce immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies. High IgE levels promote allergies and also seem to play a role in the development of atopic dermatitis. In a small study, taking vitamin E was able to alleviate atopic dermatitis symptoms and improve quality of life. 5
The supply of vitamin C correlates with the severity of neurodermatitis. 6
Selenium is a component of many antioxidant enzymes. Initial studies indicate that taking selenium can alleviate the symptoms of neurodermatitis. 7 Germany is considered a selenium deficiency area and a deficiency is widespread.
Curcumin
Curcumin is derived from turmeric and also has anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative properties. There is evidence that curcumin can have a positive effect on skin health. 8
Conclusion: Micronutrients play an important role in neurodermatitis
Inflammatory reactions are more common in neurodermatitis. Neurodermatitis patients are often not well supplied with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant nutrients. Those affected should ensure they have a good supply of these critical nutrients.
WE HAVE GONE YOU A 10% VOUCHER FOR OUR
ZINC , SELENIUM , TURMERIC , VITAMIN C , VITAMIN D AND OMEGA-3
PROVIDED AND HOPE TO BRING YOU JOY WITH IT.
SIMPLY COPY THE FOLLOWING COUPON CODE
AND ENTER IT AT CHECKOUT:
HAUT+V10
TO THE PRODUCTS
1 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24473704/
2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25282565/
3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25282565/
4 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22395583/
5 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25282565/
6 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27478546/
7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20503922/
8 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6770633/

Endometriosis: What role do nutrients and nutrition play?
In endometriosis, cells from the uterine lining also grow outside the uterus, such as in the ovaries, intestines and bladder. Endometriosis is associated with severe menstrual pain and can affect fertility.
The cause of endometriosis is not clearly understood. Genetic predisposition appears to play a role. Scientists suspect that hormonal changes and environmental toxins can also promote endometriosis. Diet is also important in endometriosis. Women with endometriosis often lack essential nutrients, which is suspected of promoting endometriosis.
The treatment of endometriosis focuses mainly on alleviating symptoms. Pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory drugs are often used. Hormones are also used in the treatment of endometriosis, such as progestogens. Taking the contraceptive pill can also alleviate endometriosis symptoms. In extreme cases, endometriosis lesions can be surgically removed.
The following nutrients are promising for endometriosis:
Omega-3
Inflammation appears to be at least partially responsible for the pain in endometriosis. Omega-3 fatty acids have an anti-inflammatory effect and can thus counteract inflammatory pain.
Poor supply of omega-3 fatty acids is associated with an increased risk of endometriosis. 1
Vitamins C and E
Endometriosis is associated with oxidative stress and inflammation. These are partly caused by endometriosis. But there is also evidence that free radicals and inflammation can drive and worsen the disease.
In a large-scale study, a low intake of antioxidant vitamins such as vitamin C and E was associated with an increased risk of endometriosis. Conversely, in a small study with endometriosis patients, chronic pain decreased and oxidative stress was reduced after taking vitamin C and E. 2 However, further research is needed here.
B vitamins
Women with endometriosis often have elevated homocysteine levels. Homocysteine is a toxic metabolic product that the body must detoxify. To do this, it needs B vitamins , especially vitamin B6, folic acid (vitamin B9) and vitamin B12 . 3 Too high a homocysteine level is often due to an inadequate supply of one or more of these B vitamins. Too much homocysteine damages the whole body and increases the risk of many diseases such as cardiovascular disease, dementia and depression.
Women with endometriosis should therefore have their homocysteine levels checked and ensure they have a good supply of B vitamins.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is not only important for bone health. It also has important functions in the immune system and helps regulate inflammation. The reproductive organs have many vitamin D receptors and a good supply of vitamin D promotes hormonal balance.
The research here is not entirely clear, but a lack of vitamin D appears to increase the risk of endometriosis. 4 In one study, the severity of period pain decreased significantly after 8 weeks of taking vitamin D. 5
Curcumin
Curcumin is extracted from turmeric and is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Curcumin also appears to have other effects on endometriosis. At least in animals, curcumin can inhibit the growth of the uterine lining and can therefore probably contain endometriosis lesions. 6 However, further research is needed to show whether this is also the case in humans.
Conclusion: Important nutrients are often lacking in endometriosis
Endometriosis is associated with oxidative stress and inflammation. These are caused by the disease, but also appear to be able to make endometriosis worse. Therefore, a good supply of anti-inflammatory nutrients is important. Women with endometriosis often lack essential anti-inflammatory nutrients such as vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin C and vitamin E. Those affected should therefore ensure they have a good supply of these nutrients.
WE HAVE GONE YOU A 10% VOUCHER FOR OUR
Vitamin B Complex , Vitamin B12 , TURMERIC , Vitamin C , VITAMIN D AND OMEGA-3
PROVIDED AND HOPE TO BRING YOU JOY WITH IT.
SIMPLY COPY THE FOLLOWING COUPON CODE
AND ENTER IT AT CHECKOUT:
ENDO+V10
TO THE PRODUCTS
1 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22562031/
2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34122682/
3 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33992189/
4 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27809683/
5 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5189720/
6 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32244563/

Liver, heart, kidney & co – how healthy are offal?
Offal has been part of the diet for thousands of years and is still eaten regularly in many countries today.
When it comes to supplying essential nutrients, it makes a lot of sense to eat offal regularly. Offal is one of the most nutrient-rich foods there is. Compared to most other foods, it provides significantly more essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, trace elements and high-quality protein.
In our culture, however, offal has become a rarity. Today, we eat mostly muscle meat. Although liver is considered a delicacy, it is relatively rare to see it. Other organs are even harder to find.
For our ancestors, however, it was the other way around. They preferred offal such as heart, liver, kidneys, lungs, tongue, brain and other organs. Muscle meat was eaten last and was also the meat most likely to be fed to dogs.
What nutrients do offal contain? Each organ has its own nutrient profile.
liver
Liver is by far the best source of vitamin A. Liver is also rich in vitamin B12 and other B vitamins . 1
In our article about liver you will learn more about which nutrients liver contains and why it is so healthy.
kidney
Kidney is incredibly rich in vitamin B12. 100 g of beef kidney contains almost 5 times the daily requirement of vitamin B12! 2
Kidney is also a good source of vitamin B3, selenium , iron, zinc , copper, potassium and phosphate. It even contains some vitamin D.
Heart
Heart is one of the best sources of coenzyme Q10 . Coenzyme Q10 has important functions in energy metabolism and is also an effective antioxidant. The body can produce coenzyme Q10 itself, but production decreases significantly with age.
Heart is also rich in collagen and the amino acid glycine.
spleen
Spleen contains a lot of iron. 3 The iron in the spleen is heme iron, which has a much better bioavailability than plant-based iron. This means that the body can absorb and utilize it much better.
For this reason, it is difficult to meet iron requirements on a vegetarian or vegan diet. This is particularly true for women, as they have a higher iron requirement than men.
pancreas
The pancreas also has a lot to offer in terms of nutrients: it is very rich in vitamin B12 and vitamin B5. It also provides considerable amounts of selenium, phosphate and zinc. 4
Include more offal in your diet
There are many good reasons to eat more offal. The problem is that it is not for everyone. We are simply no longer used to eating offal and its taste and consistency are very different from muscle meat.
The heart and tongue are very beginner-friendly as they are also muscles, so if you want to try offal, this would be a good place to start.
Liver has a relatively strong taste of its own, but is still good for beginners. It is considered a delicacy. For this reason, it is relatively common to find it in restaurants. There are also many good recipes for liver. Liver sausage is also a good way to incorporate liver into your diet.
1 Beef, variety meats and by-products, liver, raw Nutrition Facts & Calories (self.com)
2 Beef, variety meats and by-products, kidneys, raw Nutrition Facts & Calories (self.com)
3 Beef, variety meats and by-products, whimsy, raw Nutrition Facts & Calories (self.com)
4 Beef, variety meats and by-products, pancreas, raw Nutrition Facts & Calories (self.com)